Forensic Insights into Apple Watch Data Extraction
November 30th, 2023 by Oleg Afonin
Category: «General»
The latest update to the iOS Forensic Toolkit has expanded data extraction support for older models of Apple Watch, introducing low-level extraction capabilities for Apple Watch Series 0, Series 1, and Series 2. In a landscape where new devices are released on a yearly schedule, we stand committed to a balanced approach. While it’s easy for many to dismiss older devices, we recognize their significance as they frequently reappear in the labs of forensic experts. It is important to emphasize that, unlike many, we cater to the needs of experts who have to deal with legacy devices. This enhancement enables macOS and Linux users to delve deeper into these watches, retrieving crucial information such as passwords and complete file systems.
The role of wearable devices in mobile forensics
Wearable devices such as Fitbit, Apple Watch, and countless models of watches and fitness trackers made by various manufacturers, are becoming key players in criminal investigations. Information extracted from wearable devices provides valuable insight that aids both prosecution and defense. These devices have been pivotal in several cases, where Fitbit steps did not match the accused’s version of events, and Apple Watch activity data established critical timelines in murder investigations. Prosecutors have utilized health and location data from the suspect’s Apple Watch to support charges and disprove alibi, showcasing their significance in legal proceedings. For mobile forensic specialists, understanding the importance and potential of this data alongside with technical limitations is crucial in providing accurate insights and support in investigations and court proceedings.
Information available in Apple Watch
The Apple Watch is a highly sophisticated companion device built with a powerful SoC and equipped with sizable amounts of storage. The wearable is powered with watchOS, an operating system derived from iOS. Being such a powerful device, it is no wonder that the Watch can store a lot of valuable data. The low-level extraction allows accessing the entire set of data available in the Apple Watch. The extracted data includes an image of the file system and a copy of the keychain, which contains the user’s passwords. Analyzing the file system helps gain access, among other things, to the following types of data:
- Comprehensive health and activity data
- Comprehensive location history
- Keychain
- System events: network usage, app activity, watch unlocks, contact access, Bluetooth events etc.
- Messages: SMS and iMessage
- Contacts
- Wallet (tickets, boarding passes, discount cards etc.)
Apple Watch extraction methods
There are two extraction methods available for Apple Watch devices: low-level extraction based on a bootloader exploit, and logical extraction.
Bootloader-level extraction is based on the checkm8 exploit, which is available for four generations of Apple Watch up to and including Apple Watch Series 3. checkm8 extraction makes it possible to obtain the full file system image and extract a copy of the keychain. Unlike IoT devices such as the HomePod or Apple TV, the Watch can be protected with a passcode, which is one requirement for synchronizing the keychain from the paired iPhone. More on that in checkm8 Extraction of Apple Watch Series 3.
Low-level extraction via a bootloader exploit can only be used on old models of Apple Watch devices, supporting Apple Watch S0, S1, S2, and S3. For newer models of Apple Watch low-level extraction is unavailable; logical extraction must be used instead. The Apple Watch does not have a backup service (watch backups are created and stored on the paired iPhone), so only a limited amount of data can be extracted, including some system and diagnostic logs and some media files.
Both logical and low-level extraction methods require connecting the Watch to the computer, which is generally done with the help of an adapter (Apple Watch Forensics: The Adapters and Apple Watch Forensics: More on Adapters). The latest models of Apple Watch starting with Series 7 no longer come with the hidden diagnostic port, which makes it difficult or even impossible for anyone but Apple to connect these devices to a computer. This in turn means that logical extraction is only supported for Apple Watch Series 4, Series 5, Series 6, and Apple Watch SE (1st generation) devices.
In the table below, Apple Watch models compatible with low-level extraction (checkm8) are marked with green, while models listed in red only support logical extraction. Unlisted models are not supported at all (e.g. Apple Watch Series 7, Series 8, Ultra).
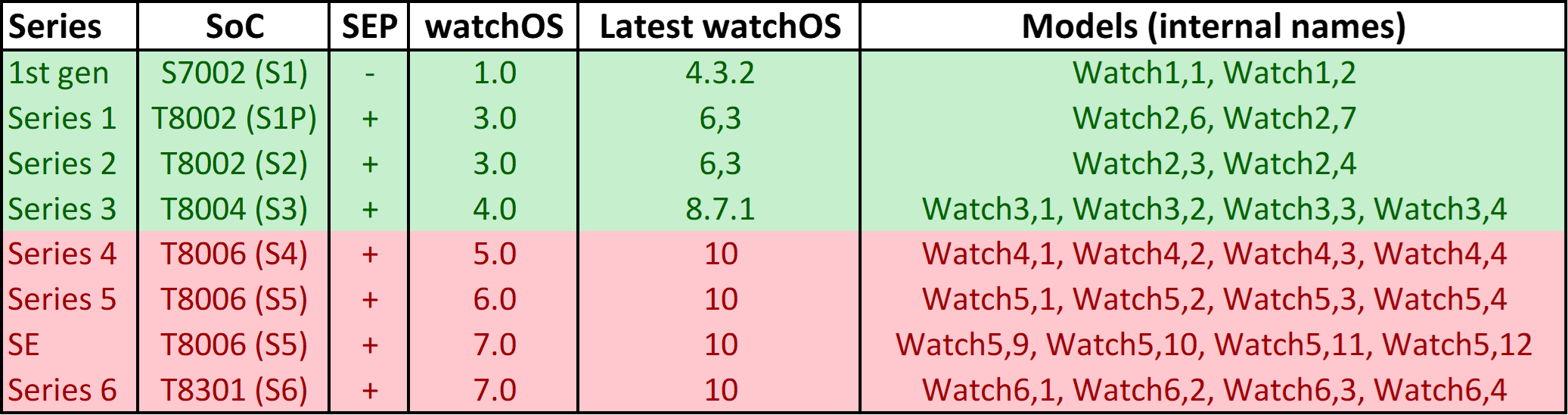
Extracting and analyzing Apple Watch data
The newly added models, which include Apple Watch S0, S1, and S2, utilize the same checkm8-based extraction mechanism we introduced earlier for the Apple Watch 3. Detailed instructions are provided in the following articles:
For analyzing the extracted content, please refer to the following articles:
When it comes to very old devices such as the original Apple Watch (Series 0), one has to be patient. The S0 takes good five minutes to boot the ramdisk, and it is very picky about adapters and cables. You must have a rock solid connection to apply the exploit, and even placing the watch into DFU may take several tries (and each attempt will be painfully slow). We strongly recommend using Recovery first, and then DFU.
Here’s how to place the Watch into DFU:
- Run EIFT in wait mode (-w)
- Connect the Watch to a PC using adapter (pairing not required)
- Press and hold both buttons
- Wait until the screen goes black, then wait for exactly 2 seconds
- Keep holding the digital crown, release the other button
- EIFT will automatically detect connected device in DFU mode
Additional information
We collected several links on the matter of wearables forensics. We strongly recommend checking out at least the first article linked.