Spoiler: you are probably already using AI agents, even if marketing hasn’t yelled at you about it yet. Forget the dark ages of 2023 when large language models (LLMs) just confidently hallucinated fake server logs and nonexistent IP addresses. Today’s AI can spin up a virtual environment, navigate web pages, scrape data, and logically process what it finds. Let’s cut through the noise and talk about what “agents” actually are, how “Deep Research” operates, and how to spin up your own pocket investigator that doesn’t come with corporate safety bumpers.
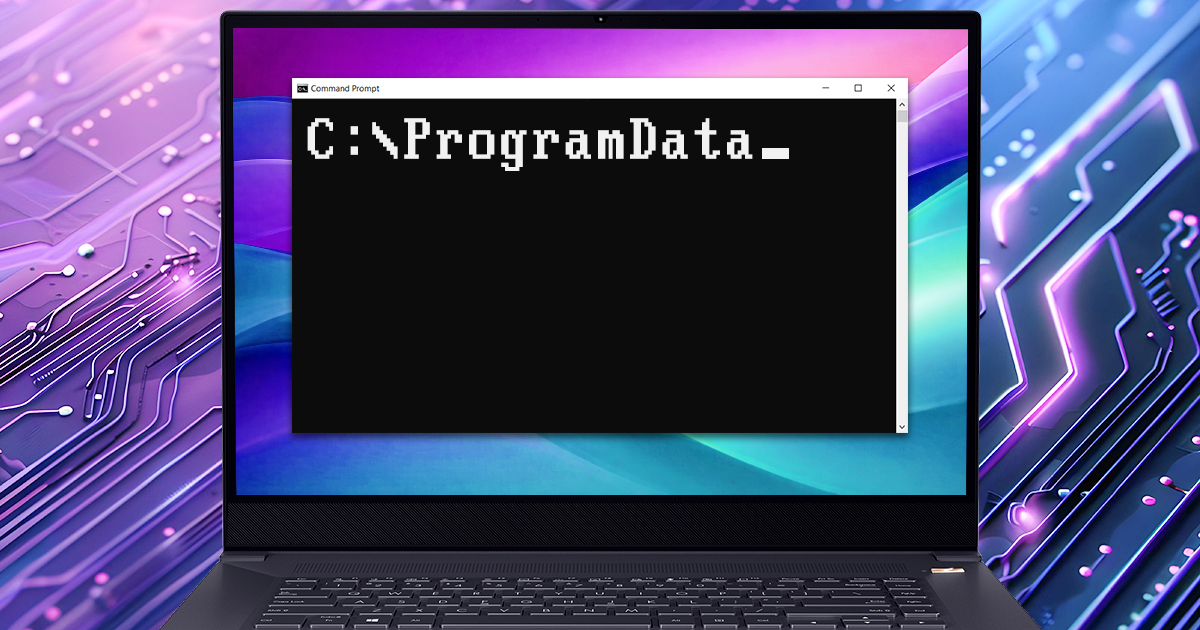
This guide continues our ongoing series exploring Windows digital artefacts and their practical value during an investigation. Here, we turn our attention to the specific set of files located under the root path %ProgramData% (commonly C:\ProgramData\) and its subfolders. Unlike standard user profile folders, this directory typically houses system-wide data, shared application configurations, and background service caches that apply to the system as a whole. For investigators, this path offers a system-level perspective. Analyzing it can uncover historical activity, revealing events from background file transfers and software installations to Wi-Fi connections and security tool detections.
This guide continues our ongoing series exploring digital artifacts found on Windows computers and their practical meaning during an investigation. With each new topic, the puzzle becomes more complex because these traces rarely exist in isolation. Modern forensic best practices rely heavily on cross-checking different types of artifacts against one another. By connecting these dots, investigators do more than just establish isolated facts – they build a solid, reliable conclusion that can stand up in court.
With massive external hard drives and smartphones everywhere, the USB interface continues to be a major channel for data theft and malware infections. For anyone working in digital forensics and incident response, building a solid timeline of when a USB device was plugged in, used, and removed is often essential. Whether you are investigating a departing employee who might have copied sensitive intellectual property to a thumb drive, or tracing a ransomware outbreak, the answers frequently involve external storage.
The discipline of digital forensics and incident response relies fundamentally on the persistent, systemic traces left by both legitimate users and malicious actors. The Windows Event Log system serves as a primary chronological record of operating system activity, capturing security events, application behaviors, service and driver activity, and user authentication telemetry. Due to the immense volume of background events generated by Windows 10 and Windows 11, isolating forensically relevant artifacts is a highly specialized task. A comprehensive understanding of this logging mechanism is often decisive when reconstructing an incident timeline.
The Windows Registry remains one of the most information-dense repositories for reconstructing system activity and user behavior. Far more than a configuration database, it serves as a critical historical record of execution, data access, and persistence mechanisms across Windows 10 and 11. While automated forensic tools are essential for extracting and parsing this data, the correct interpretation of the results remains the responsibility of the investigator. This article focuses on the Registry keys that possess distinct forensic significance. We will move beyond the standard enumeration found in legacy guides to establish the specific links between technical artifacts and their value in an investigation, distinguishing between actionable evidence and system noise.
The first steps of an investigation are rarely straightforward. Do you shut down the system and image the storage media, taking the safe but slow traditional path? Do you run a triage tool on the live system to grab passwords and keys, or do you reboot into a clean forensic environment? Traditional wisdom might suggest pulling the plug to preserve the state of the disk, but modern encryption makes this increasingly difficult. During the initial stage of an investigation, the choice usually falls between two primary strategies: deploying a live triage tool on the running system or booting into a clean, external environment.
Windows Defender and forensic triage tools often find themselves at odds. While endpoint protection is designed to lock down a system against unauthorized access, forensic utilities must access everything, including locked system files, to secure evidence. This conflict creates immediate operational risks during live analysis. Modern antivirus engines with aggressive heuristics may flag legitimate forensic binaries as malware, terminating the acquisition process or quarantining the tool itself. Beyond simple blocking, active background scanning introduces significant I/O latency and threatens the integrity of the evidence; the AV might delete or modify a suspicious file, such as a malware payload, moments before it can be preserved.
During the last decade, the evolution of charging standards in consumer electronics has been defined by an attempt to develop a single, unified power delivery interface centered around the USB Type-C connector. Historically, power delivery was characterized by a clear separation between data interfaces and dedicated power connectors. The Universal Serial Bus (USB) was originally introduced in the mid-1990s as a data bus for low-speed peripherals, with power capabilities capped at levels intended to support mice and keyboards rather than charge batteries – never intended to power demanding hardware.
In modern investigations, the web browser is no longer just an application – it is a comprehensive journal of a suspect’s life, intentions, and habits. While end-to-end encrypted clouds and locked smartphones often hit a dead end, the desktop web browser remains one of the most significant grounds for digital evidence, often serving as the silent witness that helps solve a case.