This guide continues our ongoing series exploring digital artifacts found on Windows computers and their practical meaning during an investigation. With each new topic, the puzzle becomes more complex because these traces rarely exist in isolation. Modern forensic best practices rely heavily on cross-checking different types of artifacts against one another. By connecting these dots, investigators do more than just establish isolated facts – they build a solid, reliable conclusion that can stand up in court.
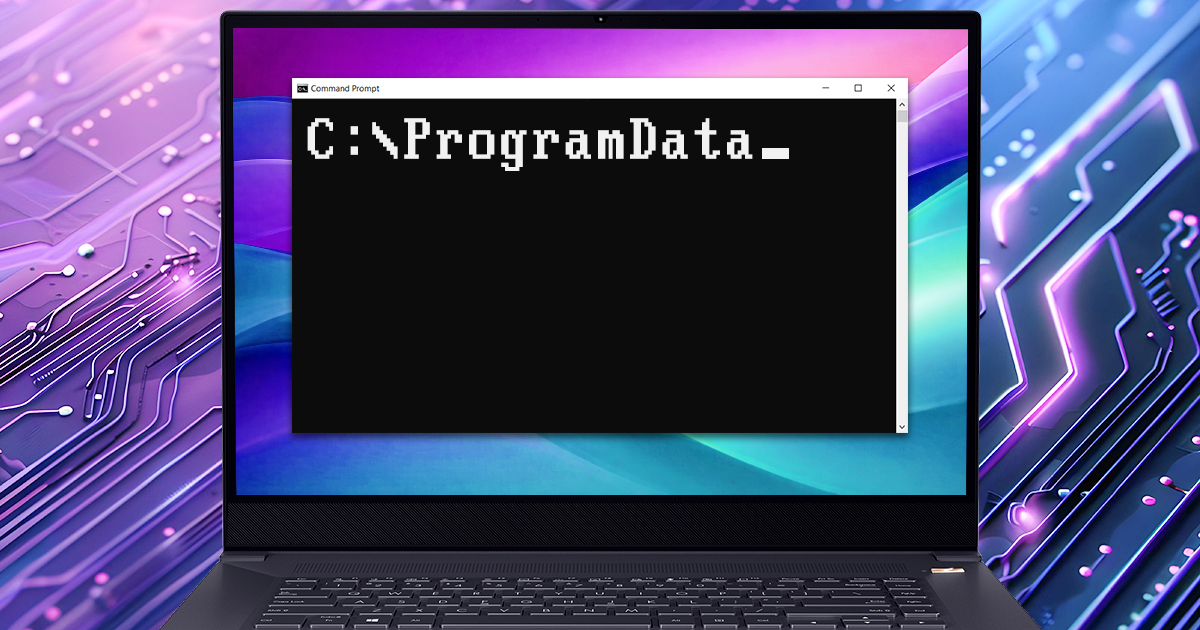
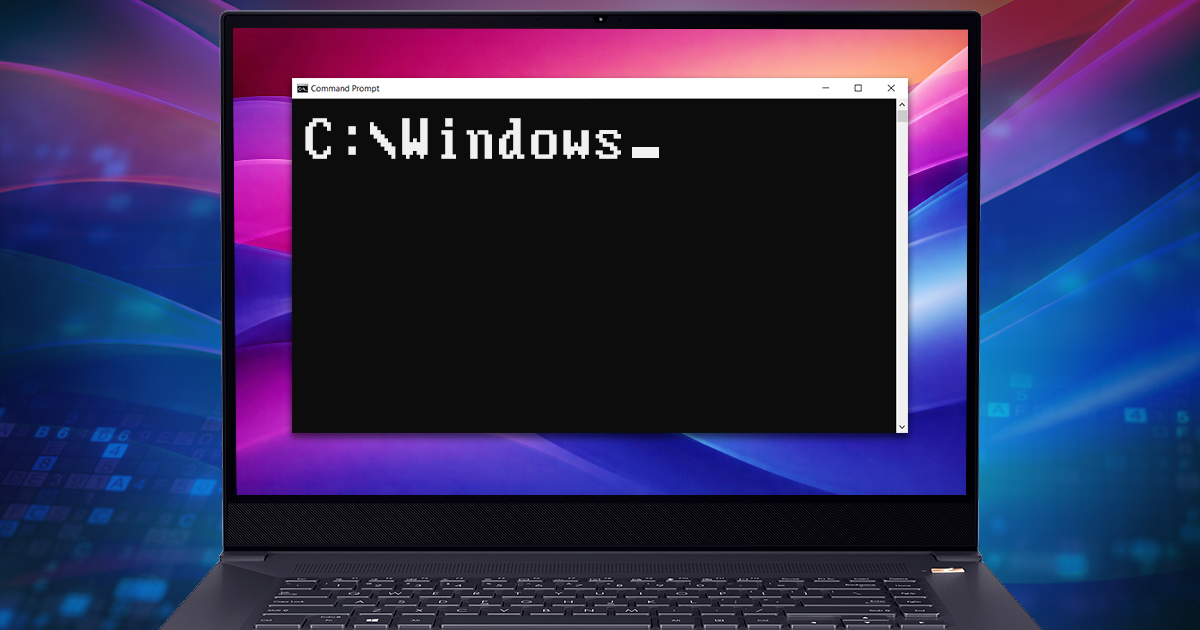
The Windows Registry remains one of the most information-dense repositories for reconstructing system activity and user behavior. Far more than a configuration database, it serves as a critical historical record of execution, data access, and persistence mechanisms across Windows 10 and 11. While automated forensic tools are essential for extracting and parsing this data, the correct interpretation of the results remains the responsibility of the investigator. This article focuses on the Registry keys that possess distinct forensic significance. We will move beyond the standard enumeration found in legacy guides to establish the specific links between technical artifacts and their value in an investigation, distinguishing between actionable evidence and system noise.
Microsoft has officially announced that newly created Microsoft Accounts will now be passwordless by default for “simpler, safer sign-ins”. This change extends the direction set by Windows 11, where traditional passwords have been gradually phased out in favor of more secure and user-friendly authentication methods – such as PIN codes, biometrics, and passkeys. In this article, we will evaluate the forensic implications of this move.
The Windows 11 24H2 update introduced a change in Microsoft’s approach to disk encryption, a shift that will have long lasting implications on digital forensics. In this release, BitLocker encryption is automatically enabled on most modern hardware when installing Windows when a Microsoft Account (MSA) is used during setup. Encryption starts seamlessly and silently in the background, covering even Home editions and consumer devices such as desktop computers that historically escaped full-disk encryption defaults.
Low-level extraction enables access to all the data stored in the iOS device. Previously, sideloading the extraction agent for imaging the file system and decrypting keychain required enrolling one’s Apple ID into Apple’s paid Developer Program if one used a Windows or Linux PC. Mac users could utilize a regular, non-developer Apple ID. Today, we are bringing this feature to Windows and Linux editions of iOS Forensic Toolkit.
iOS Forensic Toolkit comes in three flavors, available in macOS, Windows, and Linux editions. What is the difference between these edition, in what ways is one better than the other, and which edition to choose for everyday work? Read along to find out.
We have exciting news: iOS Forensic Toolkit 8 is now available for Windows users in the all-new Windows edition. The new build maintains and extends the functionality of EIFT 7, which is now approaching the end of its life cycle. In addition, we’ve made the Toolkit portable, eliminating the need for installation. Learn what’s new in the eights version of the Toolkit!
In the world of digital investigations, the sheer volume of data and the challenge of identifying valuable evidence can be overwhelming. Often, investigators find themselves faced with the need for optimization — the ability to quickly and seamlessly identify what is valuable and requires further examination. We aim to fulfill this need by introducing a new forensic toolkit in Elcomsoft System Recovery, a powerful bootable tool designed to speed up investigations, quickly identify and collect digital evidence right on the spot.
Access to encrypted information can be gained through various methods, including live system analysis (1 and 2), using bootable forensic tools, analysis of sleep/hibernation files, and exploiting TPM vulnerabilities, with password recovery being the last option on the list. Each method has different resource requirements and should be used in order of least resource-intensive to most time-consuming, with password recovery as the last resort. Familiarize yourself with the different encryption recovery strategies and learn about data formats with weak protection or known vulnerabilities.
Windows account passwords, or NTLM passwords, are among the easiest to recover due to their relatively low cryptographic strength. At the same time, NTLM passwords can be used to unlock DPAPI-protected data such as the user’s passwords stored in Web browsers, encrypted chats, EFS-protected files and folders, and a lot more. In this article we argue about prioritizing the recovery of NTLM hashes over any other types of encrypted data.