Since early days of iOS, iTunes-style system backups could be protected with a password. The password was always the property of the device; if the backup was protected with a password, it would come out encrypted. It didn’t matter whether one made a backup with iTunes, iOS Forensic Toolkit or other forensic software during the course of logical acquisition; if a backup password was enabled, all you’d get would be a stream of encrypted data.
Even today, seizing and storing portable electronic devices is still troublesome. The possibility of remote wipe routinely makes police officers shut down smartphones being seized in an attempt to preserve evidence. While this strategy used to work just a few short years ago, this strategy is counter-productive today with full-disk encryption. In all versions of iOS since iOS 8, this encryption is based on the user’s passcode. Once the iPhone is powered off, the encryption key is lost, and the only way to decrypt the phone’s content is unlocking the device with the user’s original passcode. Or is it?
Tired of reading on lockdown/pairing records? Sorry, we can’t stop. Pairing records are the key to access the content of a locked iPhone. We have recently made a number of findings allowing us to extract even more information from locked devices through the use of lockdown records. It’s not a breakthrough discovery and will never make front page news, but having more possibilities is always great.
iOS 11 has arrived, now running on every second Apple device. There could not be a better time to reminiscent how iOS forensics has started just a few short years ago. Let’s have a look at what was possible back then, what is possible now, and what can be expected of iOS forensics in the future.
“Can you unlock that iPhone?” is one of the most common questions we hear on various events and from our customers. There is no simple answer, but more often than not some options are available.
iOS forensics is always a lot of fun. Say, you’ve got an iPhone of a recent generation. It’s locked, you are blank about the passcode, and the worst part is it’s more than just the four proverbial digits (the last iOS defaults to six). And you don’t have their computer, and there is not an iCloud account either. A horror story where no one, even us, can do anything about it.
Today’s mobile devices are getting increasingly more resistant to physical imaging, mostly due to the use of full-disk encryption. Full-disk encryption makes useless some low-level acquisition techniques of yesterday, which includes JTAG and chip-off.
Accessing the list of apps installed on an iOS device can give valuable insight into which apps the user had, which social networks they use, and which messaging tools they communicate with. While manually reviewing the apps by examining the device itself is possible by scrolling a potentially long list, we offer a better option. Elcomsoft Phone Viewer can not just display the list of apps installed on a given device, but provide information about the app’s version, date and time of acquisition (first download for free apps and date and time of purchase for paid apps), as well as the Apple ID that was used to acquire the app. While some of that data is part of iOS system backups, data on app’s acquisition time must be obtained separately by making a request to Apple servers. Elcomsoft Phone Viewer automates such requests, seamlessly displaying the most comprehensive information about the apps obtained from multiple sources.
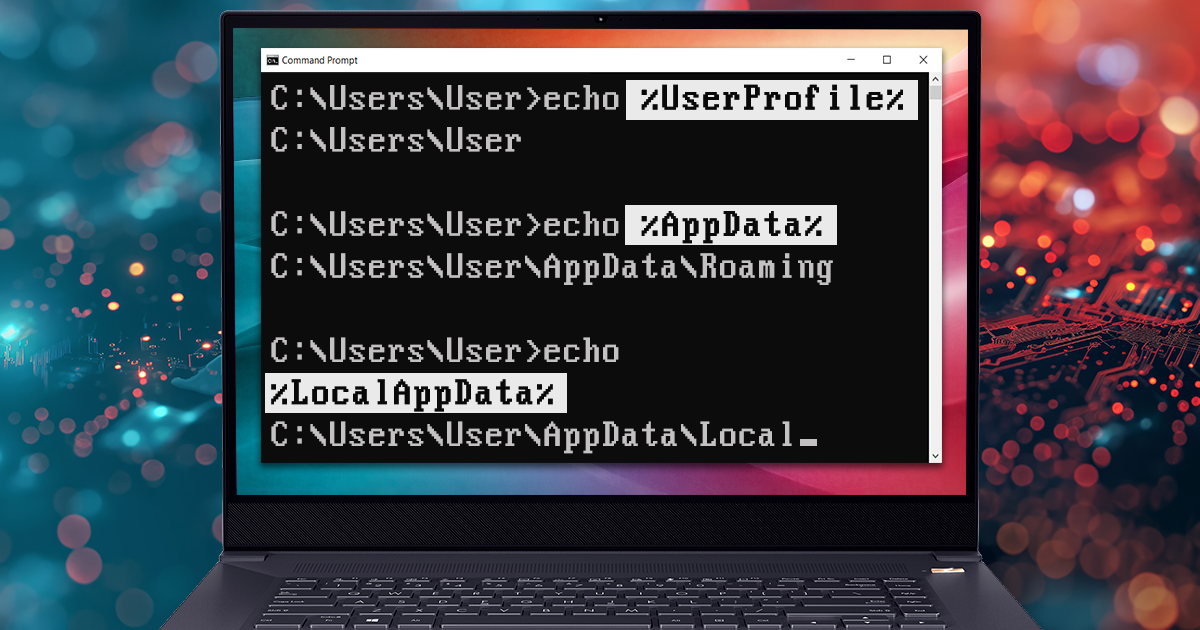
In this how-to guide, we’ll cover the steps required to access the list of saved wireless networks along with their passwords.
With all attention now being on new iPhone devices, it is easy to forget about the new version of iOS. While new iPhone models were mostly secret until announcement, everyone could test iOS 11 for months before the official release.