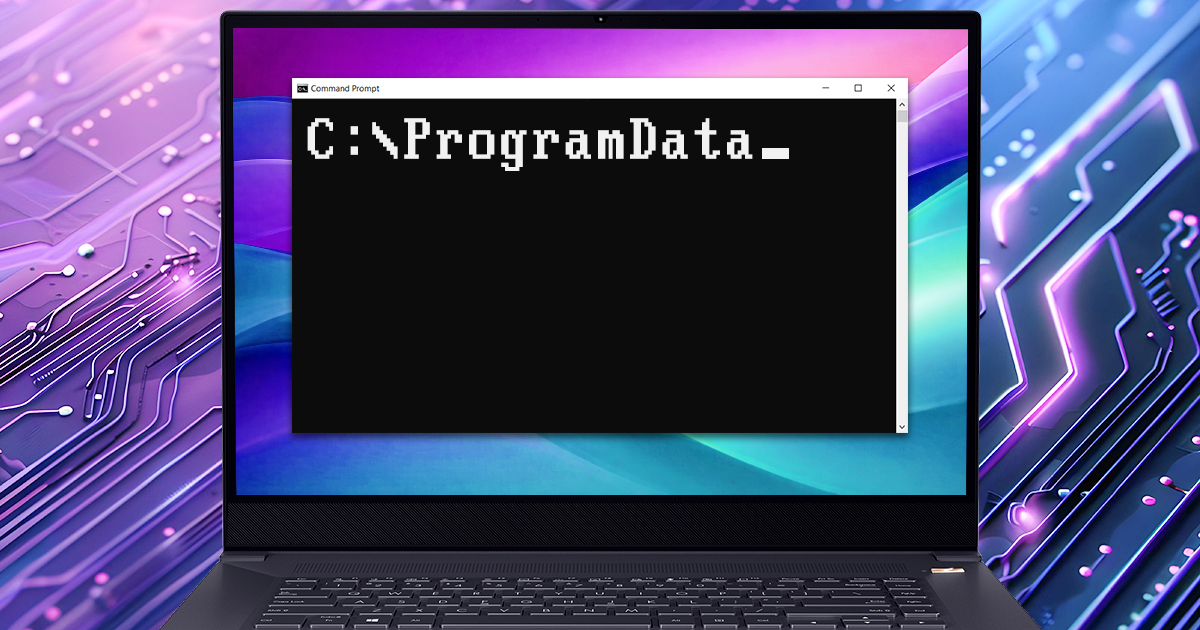
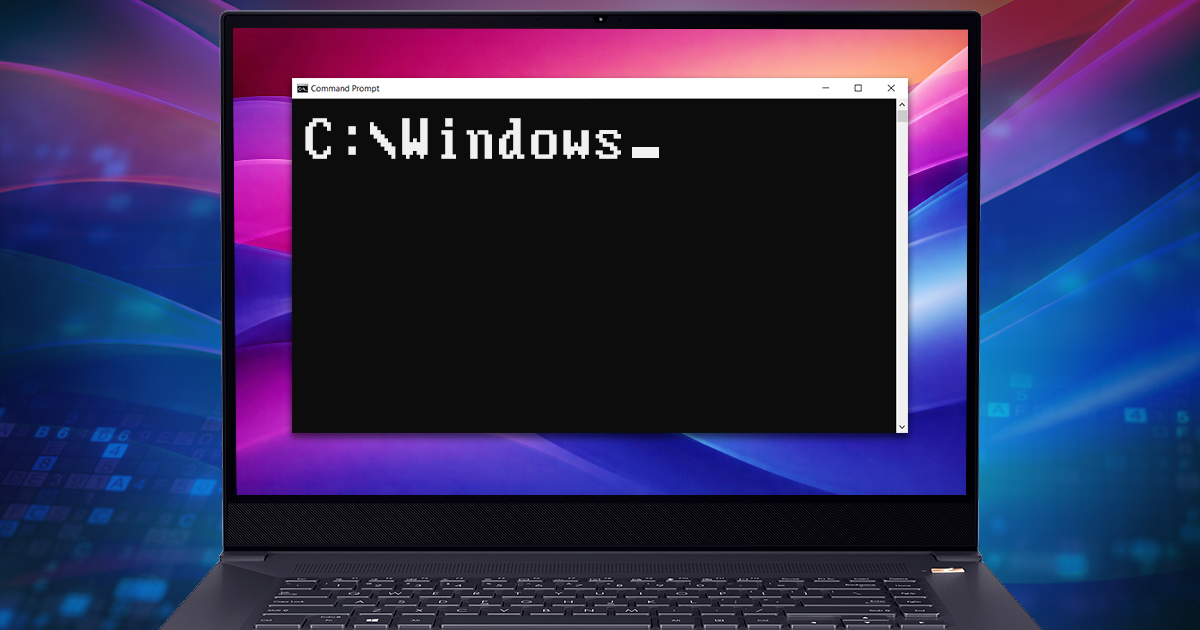
True physical acquisition is back – but only for a handful of old devices. We’re adding support for unlocking and forensically sound extraction of some of Apple’s legacy iPhones. For iPhone 4, 5, and 5c devices, we’re adding software-based passcode unlocking and device imaging functionality. Moreover, on some models you won’t even need to break the passcode in order to make a full disk image! In this walkthrough we’ll describe the steps required to image an iPhone 4, iPhone 5 or iPhone 5c device.
The Device Firmware Upgrade mode, or simply DFU, just got a second breath. The ability to image the file system, decrypt the keychain and even do passcode unlocks on some older iPhone models has been made possible thanks to the checkm8 exploit and the checkra1n jailbreak, both of which require switching the phone into DFU. The procedure is undocumented, and the steps are different for the various devices.
BFU, checkm8, checkra1n, DFU, EIFT, exploit, extraction, imaging, iOS, iPhone, passcode, recovery, unlock
The iPhone backup is one of the hottest topics in iOS forensics. iTunes-style backups are the core of logical acquisition used by forensic specialists, containing overwhelming amounts of evidence that is is unrivaled on other platforms. The backups, as simple as they seem, have many “ifs” and “buts”, especially when it comes to password protection. We wrote a thousand and one articles about iOS backup passwords, but there is always something fresh that comes out. Today we have some new tips for you.
The Screen Time password has been long recommended as an extra security layer. By setting a Screen Time password without any additional restrictions, Apple users could easily dodge attempts of changing or removing the screen lock passcode, resetting the iTunes backup password, or removing the activation lock. For a long time, removing the Screen Time password was not possible without either providing the original password or erasing the device. However, Apple had changed the way it works, making it possible to reset the Screen Time password with an iCloud/Apple ID password.
From time to time, we stumble upon a weird issue that interferes with the ability to install a jailbreak. One of such problems appearing literally out of the blue is the issue of being unable to remove the screen lock password on some iPhone devices. What could be the reason and how to work around the issue? Read along to find out!
The past two years have become a turning point in iOS acquisition. The release of a bootrom-based exploit and the corresponding jailbreak made BFU acquisition possible on multiple devices regardless of security patches. Another exploit covers the entire iOS 13 range on all devices regardless of their hardware revision. ElcomSoft developed a jailbreak-free extraction method for the entire iOS 9.0-13.7 range. Let’s see what low-level acquisition options are available today, and when to use what.
After adding jailbreak-free extraction for iOS 13.5.1 through 13.7, we now support every Apple device running any version of iOS from 9.0 through 13.7 with no gaps or exclusions. For the first time, full file system extraction and keychain decryption are possible on all devices running these iOS versions.
If you are familiar with iOS acquisition methods, you know that the best results can be obtained with a full file system acquisition. However, extracting the file system may require jailbreaking, which may be risky and not always permitted. Are there any reasons to use jailbreaks for extracting evidence from Apple devices?
Four years ago, we published our first book: Mobile Forensics – Advanced Investigative Strategies. We are really proud of this achievement. Do you want to know the story behind it and what’s changed since then in mobile and cloud forensics? Here are some insides (but please do not tell anyone!)
Is it possible to extract any data from an Apple Watch? It’s relatively easy if you have access to the iPhone the device is paired to, or if you have a backup of that iPhone. But what if the watch is all you have? If there is no paired iPhone, no backup and no iCloud credentials, how can you connect the Apple Watch to the computer, and can you backup the watch?