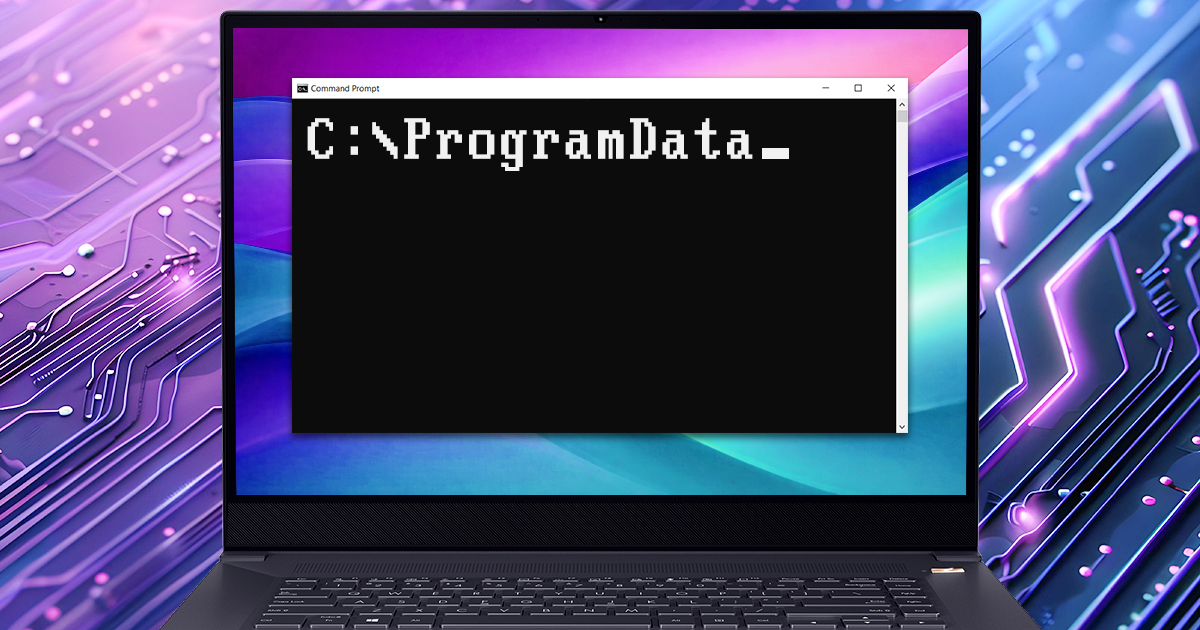
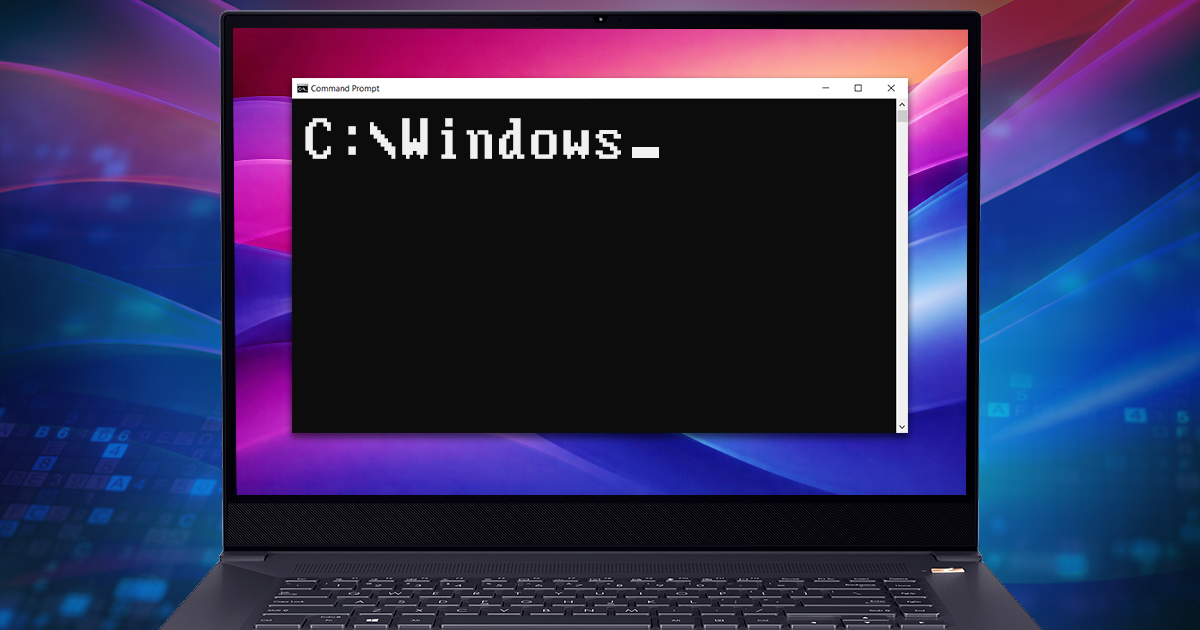
If you are familiar with breaking passwords, you already know that different tools and file formats require a very different amount of efforts to break. Breaking a password protecting a RAR archive can take ten times as long as breaking a password to a ZIP archive with the same content, while breaking a Word document saved in Office 2016 can take ten times as long as breaking an Office 2010 document. With solutions for over 300 file formats and encryption algorithms, we still find iTunes backups amazing, and their passwords to be very different from the rest of the crop in some interesting ways. In this article we tried to gather everything we know about iTunes backup passwords to help you break (or reset) their passwords in the most efficient way.
Elcomsoft Distributed Password Recovery, Elcomsoft iOS Forensic Toolkit, Elcomsoft Phone Breaker, Elcomsoft Phone Viewer, iCloud, iOS, iOS backups, iTunes, iTunes backups, jailbreak, keychain
There has been a lot of noise regarding GrayKey news recently. GrayKey is an excellent appliance for iOS data extraction, and yes, it can help access more evidence. As always, the devil is in the detail.
The two recent jailbreaks, unc0ver and Electra, have finally enabled file system extraction for Apple devices running iOS 11.4 and 11.4.1. At this time, all versions of iOS 11 can be jailbroken regardless of hardware. Let’s talk about forensic consequences of today’s release: keychain and file system extraction.
WhatsApp remains one of the most popular instant messengers. With more than 1.5 billion users and about half billion daily active users, WhatsApp sends over 100 billion messages per day. WhatsApp is secure thanks to end-to-end encryption to make intercepted messages impossible to decrypt. While this is great news to consumers and privacy advocates, it is also bad news for the law enforcement. Once an expert accepts to access the suspect’s WhatsApp communication history, they will struggle with the encryption and demand for a vendor-provided backdoor (WhatsApp: The Bad Guys’ Secret Weapon).
In Apple’s world, the keychain is one of the core and most secure components of macOS, iOS and its derivatives such as watchOS and tvOS. The keychain is intended to keep the user’s most valuable secrets securely protected. This includes protection for authentication tokens, encryption keys, credit card data and a lot more. End users are mostly familiar with one particular feature of the keychain: the ability to store all kinds of passwords. This includes passwords to Web sites (Safari and third-party Web browsers), mail accounts, social networks, instant messengers, bank accounts and just about everything else. Some records (such as Wi-Fi passwords) are “system-wide”, while other records can be only accessed by their respective apps. iOS 12 further develops password auto-fill, allowing users to utilize passwords they stored in Safari in many third-party apps.
Apple, EDPR, EIFT, Elcomsoft Distributed Password Recovery, Elcomsoft iOS Forensic Toolkit, Elcomsoft Phone Breaker, Elcomsoft Phone Digger, Elcomsoft Phone Viewer, EPB, EPD, iCloud, iOS, iTunes, jailbreak, keychain, Keychain Access, macOS
The boom in personal electronic devices recording literally every persons’ step introduced a new type of forensic evidence: the digital evidence. In this day and age, significantly more forensic evidence is available in digital form compared to physical evidence of yesteryear. Are law enforcement and intelligence agencies ready to handle the abundance of digital evidence? And more importantly, do frontline officers have the skills and technical expertise required to handle and preserve this wealth of information?
Health data is among the most important bits of information about a person. Health information is just as sensitive as the person’s passwords – and might be even more sensitive. It is only natural that health information is treated accordingly. Medical facilities are strictly regulated and take every possible security measure to restrict access to your medical records.
iMessage is undoubtedly one of the most popular instant messaging platforms for an obvious reason: it’s built in to iOS and ships with every iPhone by default. iMessage does not require complex setup, so the number of iMessage users is closely matching the number of iPhone users. Apple sells about 200 million iPhones every year, and the total number of iPhones sold is more than a billion. Unless you absolutely must chat with someone outside of Apple’s ecosystem (like those poor Android folks), you won’t need Skype, WhatsApp or Telegram. It’s also comforting to know that iMessage works everywhere around the world while most other messengers are oppressed in one or more countries.
The release of iOS 11.4.1 marked the introduction of USB restricted mode, a then-new protection scheme disabling USB data pins after one hour. The USB restricted mode was not invincible; in fact, one could circumvent protection by connecting the device to a $39 accessory. While a great improvement on itself, the new mode did not provide sufficient protection. We wished Apple maintained a list of “trusted” or previously connected accessories on the device, allowing only such devices to reset the timer. In this new iOS 12 beta, Apple makes attempts to further “improve” USB restricted mode, yet the quotes about “improving” the system are there on purpose.
It’s been a lot of hype around the new Apple security measure (USB restricted mode) introduced in iOS 11.4.1. Today we’ll talk about how we tested the new mode, what are the implications, and what we like and dislike about it. If you are new to the topic, consider reading our blog articles first (in chronological order):