On February 28, 2018, Apple has officially moved its Chinese iCloud operations and encryption keys to China. The reaction to this move from the media was overwhelmingly negative. The Verge, The Guardian, Reuters, Wired, and CNN among other Western media outlets expressed their concerns about the Chinese government potentially violating the human rights of its citizens. Politics aside, we will review Apple policies governing the Chinese accounts, and look into the technical implementation of Chinese iCloud operations. Let us see if the fears are substantiated.
We were attending the DFRWS EU forum in beautiful Florence, and held a workshop on iOS forensics. During the workshop, an attendee tweeted a photo of the first slide of our workshop, and the first response was from… one of our competitors. He said “Looking forward to the “Accessing a locked device” slide”. You can follow our conversation on Twitter, it is worth reading.
After testing waters for more than a year, Google has finally pulled the plug and began blocking access to Google Play services on uncertified devices. Why Google took this step, who is affected, and what it means for the end users? Let’s try to find out.
The iPhone X uses a new (for Apple) display technology. For the first time ever, Apple went with an OLED display instead of the IPS panels used in all other iPhones. While OLED displays have numerous benefits such as the true blacks and wide color gamut, the majority of OLED displays (particularly those made by Samsung) tend to flicker. The flickering is particularly visible at low brightness levels, causing eyestrain and headaches to sensitive users. Very few users have the slightest idea of what’s going on, attributing these health issues to oversaturated colors, the oh-so-harmful blue light and anything but OLED flickering.
In the world of mobile forensics, physical acquisition is still the way to go. Providing significantly more information compared to logical extraction, physical acquisition can return sandboxed app data (even for apps that disabled backups), downloaded mail, Web browser cache, chat histories, comprehensive location history, system logs and much more.
iOS is a locked down mobile operating system that does not allow its apps to directly access files in the file system. Unlike every other major mobile OS, iOS does not have a “shared” area in the file system to allow apps keep and share files with other apps. Yet, individual iOS apps are allowed to let the user access their files by using the file sharing mechanism.
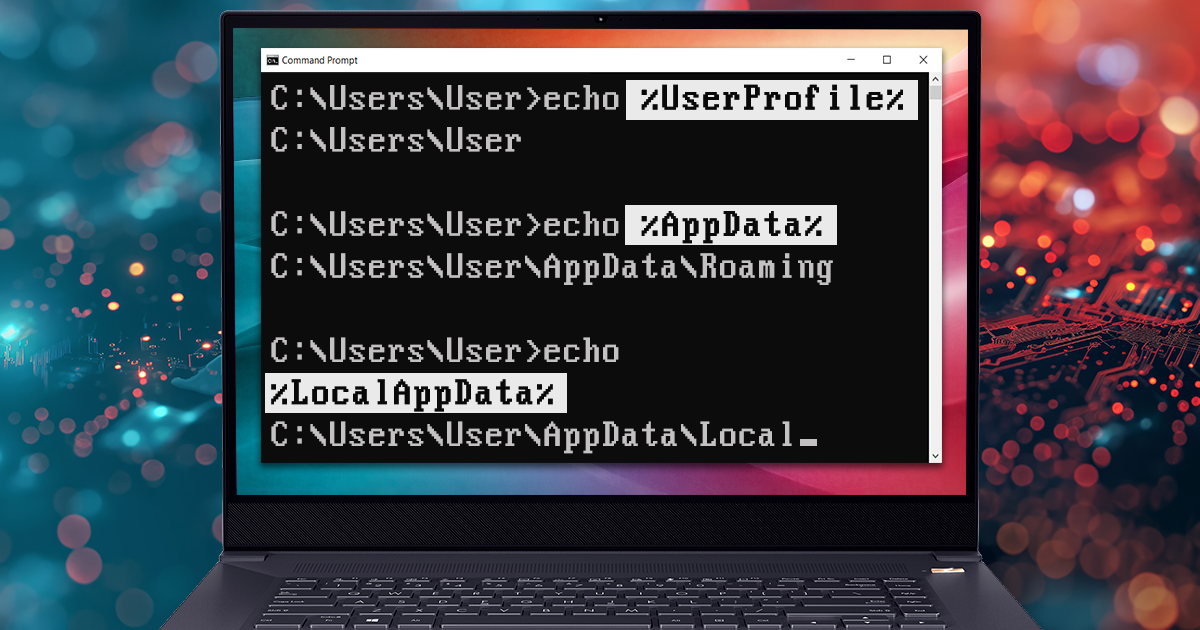
Apple has a wonderfully integrated ecosystem. Apple computers, tablets and phones conveniently synchronize information such as passwords, Web browsing history, contacts and call logs across all of the user’s devices. This synchronization mechanism uses iCloud to sync and store information. The syncing mechanism works independently from iOS system backups that are also stored in iCloud (or iCloud Drive). As opposed to daily iCloud backups, synchronized data is updated and propagated across devices in almost real time. Extracting this information can be invaluable for investigations as it provides access to the most up to date information about the user, their activities and whereabouts.
It’s been a long while since we made an update to one of our most technically advanced tools, Elcomsoft Forensic Disk Decryptor (EFDD). With this tool, one could extract data from an encrypted disk volume (FileVault 2, PGP, BitLocker or TrueCrypt) by utilizing the binary encryption key contained in the computer’s RAM. We could find and extract that key by analyzing the memory dump or hibernation files.
Forget battery issues. Yes, Apple issued an apology for slowing down the iPhone and promised to add better battery management in future versions of iOS, but that’s not the point in iOS 11.3. Neither are ARKit improvements or AirPlay 2 support. There is something much more important, and it is gong to affect everyone.